What is Audit and Assurance?
The concepts of both auditing and assurance involve the evaluation of finances. They confirm that the accounting records being kept and presented in the audit process are accurate and compliant with the standard, rules and regulations prescribed by regulatory bodies. An audit is a procedure for verifying accounting records by GAAP. Audits are governed by the law in most countries and are usually carried out by licensed and certified auditors.

Table of Contents
What is an Audit?
What is assurance?
Assurance is the process of analysing the accounts and estimating them with certainty
In addition, the audit will make sure financial records correspond to accounting standards. As well, it ensures that the accounting document is accurate. Assurance is measuring and specifying processes, procedures, etc. A large component of assurance is ascertaining the accuracy of a company’s financial statements. This activity is undertaken for the sake of preventing the misuse of funds or the perpetration of fraud. Quality assurance on the company’s financial reports confirms they comply with relevant accounting standards and is consistent with relevant accounting principles. Such rigorous quality assurance enables our company’s managers to observe and carefully examine processes, procedures, and systems, assuring that they yield a quality result.
Investors must trust the success of businesses and processes of producing credible information. It will be easier for people to make decisions or develop policies if they have reliable information or operational processes to rely on. People lose confidence in this situation when there is a lack of reliability or a high uncertainty about data and the operational processes to which the data is applied.
Key Differences between Audit and Assurance:
Assurance and Audit differ in the following ways:
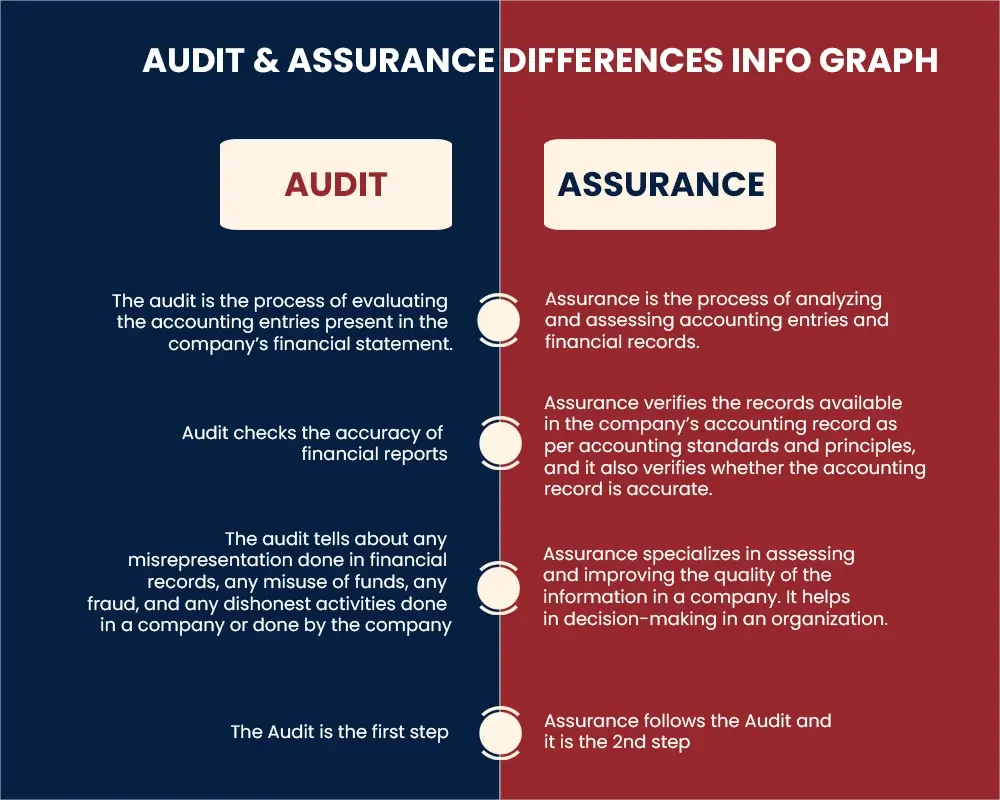
- The most basic difference between an audit and assurance is that an audit examines an organization’s books, the people in the company, and the evidence it may have, while assurance is a review of an organization’s processes and practices to know that the books and evidence are showing the true and fair view of the company.
- An audit may take place during the financial year, while assurance may take place multiple times within a year. The scope of audit encompasses both financial statements and internal control systems, while that of assurance covers only internal control systems.
- During an audit, the auditor seeks to make thorough conclusions about the financial statements of a business or individual with any available financial data. They seek to make what is called a positive conclusion. Most firms that do assurance reviews work to provide a negative conclusion, or limited assurance, meaning they find no evidence of misrepresentation.
- In an audit, the auditor makes an opinion on whether or not financial statements fairly represent to readers what they should be. On other hand, assurance provides recommendations to management on how to improve internal controls based on their findings during the process of assessment.
- The assurance follows the audit.
- An audit is performed by either an internal or external auditor, whereas assurance is performed by an audit firm.
What Types of Audit Are Available?
Auditing involves an independent third party conducting the audit – for example, an independent firm like one with certified public accountants. After the audit, a report will be shared with shareholders and stakeholders who aren’t on the team. While the specifics of an audit vary, the general benefit of an external audit is the impartiality and objectivity of the audit team. This makes the audit process and findings more credible to shareholders and external stakeholders.
Auditing involves an independent third party conducting the audit – for example, an independent firm like one with certified public accountants. After the audit, a report will be shared with shareholders and stakeholders who aren’t on the team. While the specifics of an audit vary, the general benefit of an external audit is the impartiality and objectivity of the audit team. This makes the audit process and findings more credible to shareholders and external stakeholders.
3. Financial Statement Audits
When auditing a company’s financial statements, independent auditors need to report if they align with the appropriate standards.
To do this, they must complete the following three tasks
- Assess the risks of any sort of dishonesty – intentional or unintentional.
- Assure adequate evidence has been found on whether misstatements exist.
- Form a qualified opinion on the financial statements or conclude that an opinion cannot be given.
4. Performance Audits
Many objectives can be evaluated through performance audits. An entity may request or require a performance audit for any of the following:
- Results and effectiveness of the program
- Controls within the organization
- Certain requirements must be met
- Analyses of prospective
5. Operational Audits
Operational audits analyze an organization’s activities about predetermined goals and will analyze processes, procedures, and systems. The goal of an operational audit is to measure effectiveness, efficiency, and productivity. Potential benefits of an operational audit include uncovering opportunities for improvement and developing plans for corrective actions.
6. Compliance Audits
A compliance audit occurs when an entity is evaluated for adherence to a government’s rules, standards, and requirements.
Types of Assurance Services:
Financial Assurance Services:
The internal assurance services a CPA firm provides usually involve financial projections, due diligence on the transaction involving another company, and reports on the financial condition of an individual. CPAs who work in an assurance department of a financial services company often rely on data in assessing a financial matter but they might also establish the validity of data by providing context, explaining the data’s meaning, or making data directly relevant. At times, when considering financial measurements in an examination of a company’s records, insufficient data has been used to measure one specific aspect of its finances.
Non-Financial Assurance Services:
Some assurance services are not directly related to money. For instance, assurance firms such as CPA firms can provide help with data security, performance claims, quality control, and environmental performance. With many non-financial assurance services, there are several firms involved in providing them and so not only the CPAs. Security auditing is one of those non-financial assurance services and in the area of data security, there are also information security consultancies.
Importance of Audit & Assurance Services for Business in UAE:
Auditing and assurance are not just about counting things. These numbers tell a story. Reflecting on what has been done and looking to what is to come. Audit and assurance at Deloitte are all about demonstrating how things are and exploring what’s needed to make them better.
The auditing and assurance aspect shows where you are, and gives guidance for your next step. The audits and assurances show what needs to happen for your next plan to have a chance of succeeding. All of our research provides information about what, how, and why changes are made, so you are always in the know.
1. To achieve accurate financial statements
Businesses with fewer than 50 employees don’t have a large team of accountants to ensure that they keep accurate books of accounts. A small business audit ensures that the company’s books of accounts are accurate and comply with international accounting standards.
2. In Making Better Decisions
A company’s management will be able to make better decisions if its financial statements are accurate
3. To reduce the risk of fraud
Auditors in UAE I can tell you where your company’s weaknesses lie.
4. Audit Helps to Build Trust
You can build trust among the company’s partners, investors, lenders, authorities, and other stakeholders by reviewing the financial statements periodically.
5. Verification of Statutory Compliances
The auditor will ensure that the company is compliant with commercial and export regulations, like those related to Value Added Tax (VAT), Ultimate Beneficial Owners (UBO) or Economic Substance Regulations (ESR)






